Knowing your skin phototype is essential to keep your skin healthy and radiant. This parameter, often overlooked, is in fact the basis of a correct skin care routine. Like our skin type, our skin type is also unique and determines how our skin reacts to sun exposure, pigmentation and many other environmental factors.
Skin phototype is not something we can change, but knowing it helps us make informed skin care decisions. For example, some people have skin that tans easily, while others tend to burn. These differences are determined by our skin phototype.
In this guide, we'll explore the different skin phototypes, the science behind them, and how to determine your skin phototype. We'll also discuss the importance of knowing your phototype for your health and skincare, and how sun exposure can affect skin health.
The science behind skin phototypes
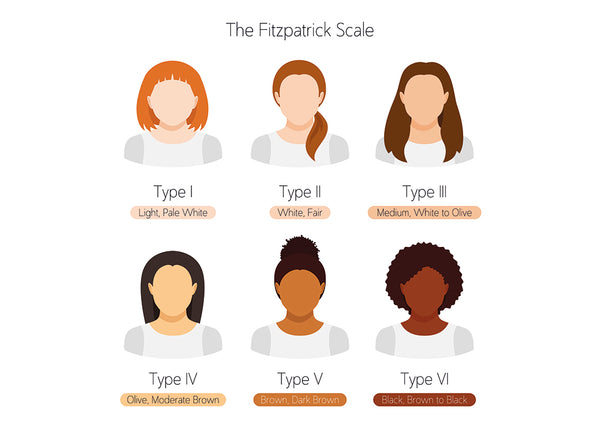
The science behind skin phototypes dates back to the 1970s, when dermatologist Thomas Fitzpatrick developed a scale to rank different skin reactions to sun exposure. This scale, now known as the Fitzpatrick Phototypic Scale, is still widely used today.
The Fitzpatrick scale classifies skin phototypes into six categories, from phototype I, which represents people with very fair skin who burn easily and rarely tan, to phototype VI, which represents people with dark skin who do not tan. never burns and tans very easily.
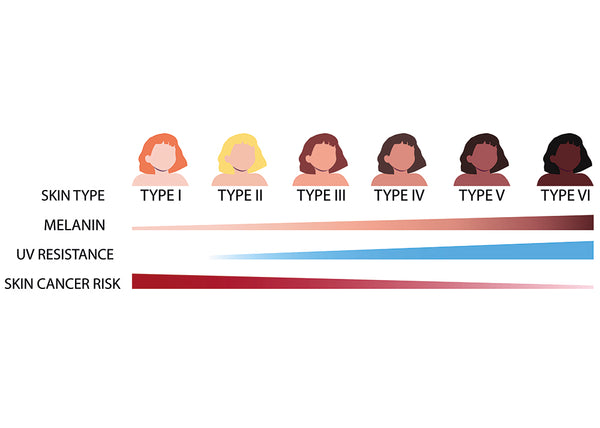
Each skin phototype has a different amount of melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin, hair and eyes. The amount of melanin in the skin determines how the skin reacts to exposure to the sun and ultraviolet rays.
The importance of knowing your skin phototype
Knowing your skin phototype is essential for a number of reasons. First, it helps us understand how our skin will react to sun exposure. For example, people with skin phototype I will need more sun protection than those with skin phototype VI.
Also, knowing your skin phototype helps us choose the skincare products that best suit us. Not all skincare products are suitable for all skin phototypes. For example, some people may have drier or oilier skin depending on their skin phototype.
Finally, knowing your skin phototype can help us prevent future skin problems. For example, people with skin phototype I or II have a higher risk of developing melanoma, a type of skin cancer, than those with skin phototype V or VI.
How to determine your skin phototype

Determining your skin phototype may seem complicated, but it's actually a fairly simple process. The most common method of determining skin phototype is through self-assessment, which involves observing how your skin reacts to sun exposure.
For example, if your skin burns easily and rarely tans, you probably have skin phototype I. On the other hand, if your skin never burns and tans very easily, you probably have skin phototype VI.
Another method to determine your skin phototype is through a professional dermatological exam. A dermatologist can evaluate your skin and determine your skin phototype through a series of tests and observations.
Detailed discussion on different skin phototypes
Different skin phototypes have unique characteristics and needs. In this section, we will explore the six skin phototypes of the Fitzpatrick Phototypic Scale in detail.
Phototype I is characterized by very fair skin, red or blond hair, and blue or green eyes. These people burn very easily and rarely tan. They also have a higher risk of developing melanoma.
Skin type II is similar to skin type I, but these people may tan slightly. They still have a high risk of sunburn and melanoma.
Skin type III is characterized by light to olive skin, brown hair and brown or green eyes. These people may tan gradually but still have a risk of sunburn.
Skin type IV is characterized by olive to brown skin, brown or black hair, and brown eyes. These people tan easily and rarely burn.
Skin type V is characterized by brown to dark skin, black hair, and dark eyes. These people tan very easily and rarely burn.
Finally, phototype VI is characterized by very dark skin, black hair, and dark eyes. These people never burn and tan very easily.
Skin health and care according to your skin phototype
Skincare should be tailored to your skin phototype. For example, people with skin phototype I or II should use a high protection factor sunscreen and be careful with sun exposure.
Conversely, people with skin phototype V or VI may use a sunscreen with a lower SPF, but should still be careful about sun exposure and have regular skin checks to monitor for any changes.
In addition to sunscreen, your skin care routine should include gentle cleansing, adequate hydration, and the use of anti-aging products as needed. It is important to choose products that are suitable for your skin phototype.
The role of sun exposure in skin health
Sun exposure has a significant impact on skin health. While a certain amount of sunshine is beneficial for vitamin D production, too much exposure can cause skin damage, including sunburn, premature aging, and melanoma.
The amount of sun exposure your skin can tolerate varies depending on your skin phototype. For example, people with skin phototype I or II have a very low tolerance to the sun and should limit their exposure. On the other hand, people with skin phototype V or VI have a higher tolerance to the sun, but should still protect their skin from excessive exposure.
Regular use of sunscreen is essential for all people, regardless of skin phototype. It is important to choose a product with an adequate sun protection factor (SPF) and apply it regularly.
Skin phototypes and potential skin problems

Every skin phototype has potential associated skin problems. For example, people with skin phototype I or II have a higher risk of developing melanoma, a type of skin cancer. These people should have regular skin checkups and see a dermatologist if they notice any changes in the skin.
People with skin phototype III or IV may have problems with hyperpigmentation, which can cause dark spots on the skin. These people should be careful with sun exposure and use products that help prevent and treat hyperpigmentation.
People with skin phototype V or VI may have problems with hyperpigmentation, which can cause pale patches on the skin. These people should see a dermatologist if they notice any changes in skin pigmentation.
Embrace your skin type for optimal skin health
In conclusion, knowing your skin phototype is essential to keep your skin healthy and radiant. This parameter, often overlooked, is the basis of a correct skin care routine.
Embracing your skin phototype means accepting how your skin reacts to sun exposure, pigmentation, and other environmental factors. It also means making informed skincare decisions, choosing the products that are best for you and your skin.
Remember, your skin is unique. Don't compare your skin to others, but rather focus on what's best for your skin. Take care of your skin, protect it from the sun, and embrace your skin type for optimal skin health.

Leave a comment